문자열 입력받기
cin
공백을 무시한다. 띄어쓰기, 엔터, 탭 등으로 입력값의 기준을 설정한다.
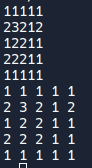
숫자를 한글자씩 잘라서 input을 받는 상황
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int N = 5;
vector<vector<int>> v(N, vector<int>(N,0));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
scanf("%1d", &v[i][j]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
cout <<v[i][j] <<" ";
cout <<endl;
}
}
istream의 cin.getline()
cin.getline(char str, streamsize n, char delim)
C언어 스타일의 문자열을 입력 받을 때 사용
n: 저장할 문자 최대 개수(널 문자 포함 값)
delim: 이 문자가 나올 경우 저장 중(지정 안할 경우 엔터가 기준)
string의 getline()
getline(istream& is, string str);
getline(istream& is, string str, char delim);
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s1, s2;
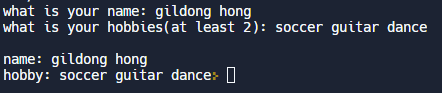
cout << "what is your name: "; // ex) 입력: gildong hong
cin >> s1 >> s2 ;
string s3;
cout << "what is your hobbies(at least 2): "; // ex) 입력: soccer guitar dance
cin.ignore(); // 입력 버퍼 지우기
getline(cin, s3);
cout<<"\n;
cout<<"name: "<<s1 <<" "<< s2<<endl;
cout<<"hobby: "<<s3;
}
char 함수
대문자 소문자 아스키 차이 32(A: 65, a:97)
tolower(), toupper() 함수 사용 가능
숫자 아스키코드 '0'은 48
꿀팁!!
대문자 -> 소문자 바꾸고 싶으면
ex
C -> c
"C"-"A"+"a"
String 함수
string::find 함수
문자열 있을 때 --> 그 문자열 시작 index 반환
문자열 없을 때 --> string::npos 반환
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s ="1 2 3 4";
int idx=s.find(" ");
cout<<"index="<<idx<<"\n"; // output: index=1
if(s.find("5")==string::npos)
cout<<"not found"; // output: not found
}
string.find("1234");
substr();
string.substr(문자열 위치, 자를개수)
형변환 방법들
string -> int
#include <string>
stoi()
int, double -> string
to_string()
데이텨 형식 범위
https://learn.microsoft.com/ko-kr/cpp/cpp/data-type-ranges?view=msvc-170
- int (unsigned int)
- __int8 (unsigned __int8)
- __int16 (unsigned __int16)
- __int32 (unsigned __int32)
- __int64 (unsigned __int64)
- short (unsigned short)
- long (unsigned long)
- long long (unsigned long long)
벡터(vector)
STL(Standard Template Library)
가변길이 배열
현재 배열의 원소 개수보다 더 공간을 할당해놓는다.
https://reakwon.tistory.com/202
초기화 방법
vector<int> v1; //아무것도 없는 비어있는 vector
vector<int> v2(5); //5개의 int형을 저장하는 vector(전부 0으로 초기화)
vector<int> v3(5,1); //5개의 int형을 저장하는 vector(전부 1로 초기화)
vector<int> v4 = { 1,2,3,4,5 }; //배열과 같은 초기화
vector<int> v5(v4); //v4의 벡터 요소를 복사해서 초기화
데이터 뒤에서 추가 및 삭제: push_back(), pop_back()
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> v = { 0,9,21,1,0,29,2022 };
vector<int>::iterator it=v.begin(); //맨앞
//v.insert(it, 90); //맨앞에 90삽입
v.insert(it + 4, 90); //4번째 원소에 90삽입
for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
cout << *it << endl;
return 0;
}
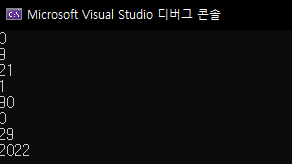
rotate();
배열 안에 있는 값들을 지정 횟수만큼 오른쪽 or 왼쪽으로 회전시킬 수 있다.
rotate(시작 반복자, 첫 위치에 올 인덱스 값, 마지막 반복자)
rotate(array.begin() ,array.begin()+1,array.end());예시. 위 방법은 왼쪽으로 1칸씩 이동.
reverse();
reverse(array.begin(), array.end())sort();
sort로 오름차순 or 내림차순으로 정리한뒤 첫번째나 끝자락 값 가져오기.
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),greater<int>) // 내림차순 ex [3, 2, 1]assign();
void assign ( InputIterator first, InputIterator last );반복자를 통해 할당 가능하다.
범위는 (이상, 미만]
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector <int> v={1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
vector <int> v2;
v2.assign(v.begin()+1, v.end());
for(auto i:v2)
cout<<i<<" "; // output: 2 3 4
}
max_element()
큰 요소
int max=*max_element(v.begin(),v.end());
2차원 벡터
https://leeeegun.tistory.com/3
선언
vector <vector<int>> v;push_back 어떻게 사용할지?
-> vector<int>형을 넣어주면 된다.
vector <vector <int>> v;
vector <int> v2;
v.push_back(v2);
접근
vector < vector <int> > v;
vector <int> v2;
v.pushback(v2);
v[0].pushback(7);
// v[0]에 담겨있는 v2 벡터에 7 입력
cout << v[0][0]; // 7 출력
cout << v.at(0).at(0); // 동일하게 7 출력
초기화
https://powerofsummary.tistory.com/21
vector<vector<int> > v1(6, vector<int>(5, 0)); // 6칸 만들고, 그 안을 vector<int>(5,0)으로 채운다
// vector<int>(5,0) : vector를 5칸 만들고, 그 안을 0으로 채운다.
v1[0][0] = 1; //벡터의 메모리가 이미 할당되어 있으니 바로 접근이 가능하다.
v1[5][4] = 20; //벡터의 메모리가 이미 할당되어 있으니 바로 접근이 가능하다.
cout << "v1[0][0] = " << v1[0][0] << '\n';
cout << "v1[5][4] = " << v1[5][4] << '\n';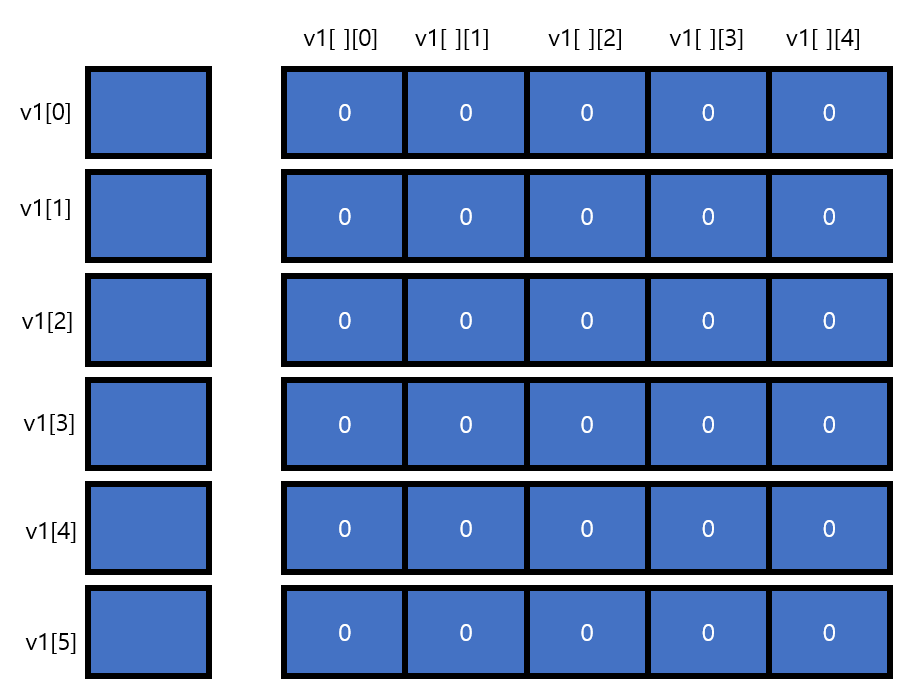
반복자(iterator)
컨테이너에 원소에 접근할 수 있는 포인터와 같은 객체
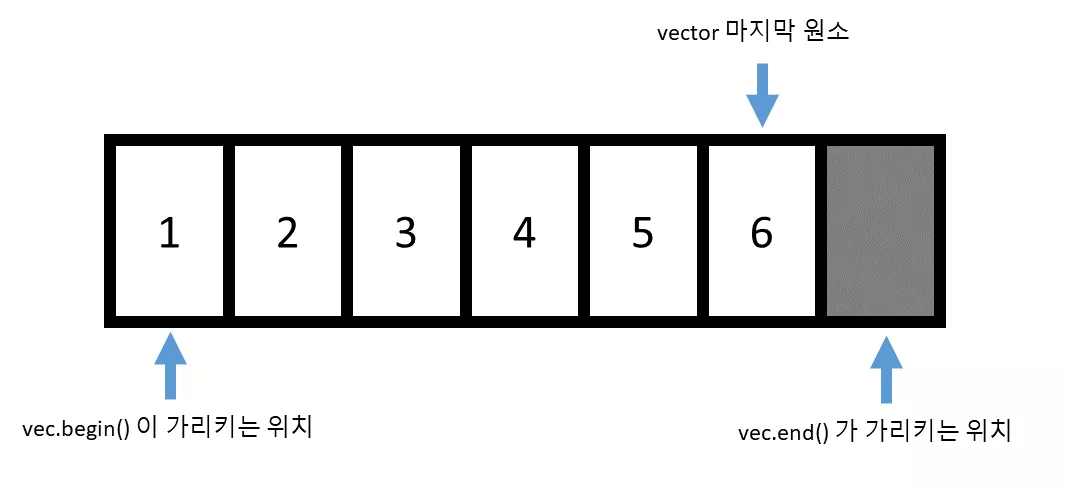
- 선언
vector<int>::iterator iter;
간단한 예시
for (std::vector<int>::iterator itr = vec.begin(); itr != vec.end(); ++itr) {
std::cout << *itr << std::endl;
}
vec.insert(vec.begin()+2,15); // vec[2] 앞에 15 추가
vec.erase(vec.begin()+3); // vec[3] 제거
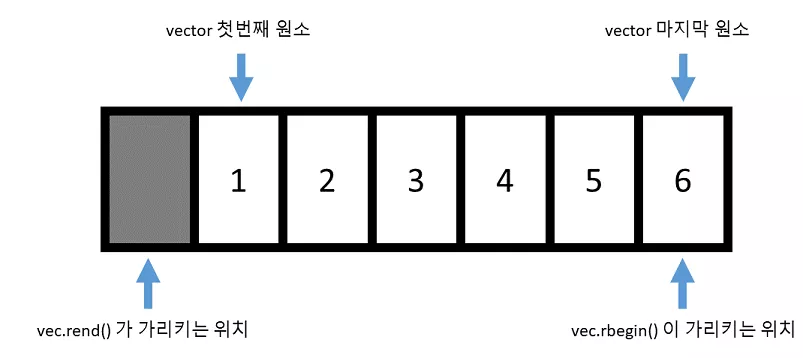
// 역반복자(reverse iterator)
std::cout << "역으로 vec 출력하기!" << std::endl;
std::vector<int>::reverse_iterator r_iter = vec.rbegin();
for (; r_iter != vec.rend(); r_iter++) {
std::cout << *r_iter << std::endl;
}
- iter index 찾기
예시
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<int>::iterator iter;
vector v={1,2,3,4,5};
int index;
iter=find(v.begin(),v.end(),2);
index=distance(v.begin(),iter);
cout<<"index = "<<index;
return 0;
}
Map
key, value 쌍으로 이루어져있다.
라이브러리
#include <map>선언하기
map<key type, value type> 이름
map<String, int> map;초기화
map<int, string> m={{1, "one}, {2,"two"}}
데이터 삽입 및 원소 수정
m[key]=val; // 원소 수정 및 데이터 삽입 가능예시
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
map<int, string> m;
m.insert(pair<int, string>(40, "me"));
m.insert(pair<int, string>(35, "Show"));
m.insert(pair<int, string>(10, "Dok2"));
m.insert(pair<int, string>(90, "6"));
m.insert(pair<int, string>(65, "money"));
m.insert(pair<int, string>(20, "ZICO"));
m.insert(pair<int, string>(50, "the"));
map<int, string>::iterator iter;
//접근방법 1
for(iter = m.begin(); iter != m.end(); iter++){
cout << "[" << iter->first << ", " << iter->second << "]" << " " ;
}
cout << endl;
//접근방법 2
for(iter = m.begin(); iter != m.end(); iter++){
cout << "[" << (*iter).first << ", " << (*iter).second << "]" << " " ;
}
return 0;
}

map 관련 함수 정리
https://blockdmask.tistory.com/87
- m.begin();
- m.end();
- m.rbegin();
- m.rend();
- m.clear();
- m.count(k);
- m.empty();
- m.insert(k); //k는 pair 객체입니다.
- m.insert(iter, k);
- m.erase(start, end);
- m.find(k): 원소 k를 가리키는 반복자 반환. 없다면 m.end() 반복자 반환
- m2.swap(m1); : m2와 m1를 바꿔준다.
- m.upper_bound(k);
- m.lower_bound(k);
- m.equal_range(k);
- m.value_comp();
- m.key_comp();
- m.size();
- m.max_size();
stringstream
헤더
#include <sstream>
예시
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
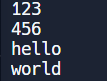
int main(){
int num;
string s;
string str1="123 456", str2="hello world";
stringstream stream1, stream2(str2);
//초기화
stream1.str(str1);
while(stream1>> num){
cout<<num<<end;
}
while(stream2>>s){
cout<<s<<endl;
}
Queue
#include <queue>선언
queue<int> q;함수들
queue.push(element);
queue.pop(); //front 요소 삭제
queue.front(); //front 반환
Priority Queue
라이브러리
#include <queue>선언
priority_queue <자료형>
priority_queue <자료형, container, 비교함수>
기본은 내림차순
priority_queue <int> pq; //내림차순
priority_queue <int, vector<int>, greater<>> pq; // 오름차순
함수 정리
pq.push(1) // 1 삽입
pq.pop(); // 맨 앞에 있는 원소(우선순위 높은 원소) 삭제
pq.top(); // 맨 앞에 있는 원소 반환
pq.size(); // size 반환
pq.empty(); // 비어있으면 true, 아니면 false
Sort()할 때, compare 함수를 통한 조건 있는 정렬?
https://cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/sort/
sort(first, last, comp)
comp는 true를 리턴하면 앞에 위치한 값이 앞에 남는다.
--> true면 위치 안바꾼다!
내림차순(ex. 3 2 1)으로 정렬하는 법
// 방법 1
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),greater());
// 방법 2
bool compare(int a, int b)
return a>b;
순서 1) 홀수 - 짝수이면서 그 중에서 오름차순
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool compare(int a, int b){
if(a%2==0 && b%2==0) //a, b 둘다 짝수일 때
return a<b; // b가 a보다 크면 바꾸지 않는다(오름차순)
else if(a%2==0) // a가 짝수일 때
return 0; // false이므로 a 짝수가 뒤로간다(바꾼다)
else if(b%2==0) // b가 짝수일 때
return 1; // true이므로 a, b 위치 바꾸지 않는다.
else // a, b 둘 다 홀수 일 때
return a<b; // b가 a보다 크면 true이고, true면 위치 안바꾼다.
}
int main() {
vector<int> v={5,4,1,2,3,3,5,6,7,8};
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),compare);
for(auto i:v)
cout<<" "<<i;
std::cout << "Hello World!\n";
}
정렬을 이용한 예시(프로그래머스: 가장 큰 수)
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
bool comp(string a,string b){
return a+b>b+a;
}
//a+b가 b+a보다 크면 true(안바꿈)
string solution(vector<int> numbers) {
string answer = "";
vector <string> string_numbers;
for(auto num:numbers)
string_numbers.push_back(to_string(num));
sort(string_numbers.begin(),string_numbers.end(),comp);
for(auto i:string_numbers)
answer+=i;
if(answer[0]=='0')
return "0";
return answer;
}vector(벡터) 중복 값 제거 방법
https://kkaeruk.tistory.com/19
unique() 함수는 중복되는 값을 뒤로 모은다. 반환 값은 뒤 부분의 iterator로 간다. 그 뒤, erase() 함수를 통해 지워준다.
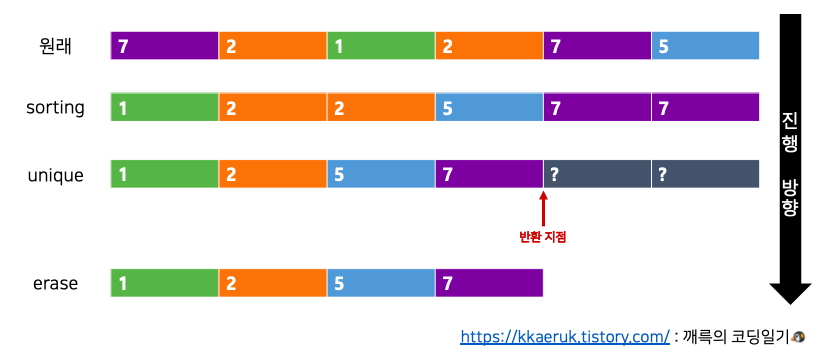
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector <int> v={1, 2, 5, 2, 6, 3, 4, 5};
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
v.erase(unique(v.begin(),v.end()),v.end());
for(auto i:v)
cout<<i<<" "; // output: 1 2 3 4 5 6
}
next_permutation 순열 구하는 법
https://mjmjmj98.tistory.com/38
정렬을 오름차순으로 무조건 해줘야 된다.
중복을 제외하고 순열을 만들어준다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector <int> v={3, 1, 1};
sort(v.begin(),v.end());
do{
for(auto i:v)
cout<<i<<" ";
cout<<"\n";
}while(next_permutation(v.begin(),v.end()));
}
조합(Combination) 구하기
https://mjmjmj98.tistory.com/38
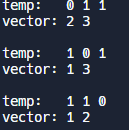
temp이라는 보조 배열을 만들어서 조합을 구한다.
여기서 temp는 1, 0으로 이루어진다. temp를 통해 next_permutation을 진행할 것이기에 정렬을 해주어야 하고, '1', '0'으로 이루어져 있기에 순서는 배제된다.
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector <int> v={1, 2, 3};
vector <int> temp={1,1,0};
sort(temp.begin(),temp.end());
do{
cout<< "temp:\t";
for(int i=0; i<temp.size();i++)
{
cout<<temp[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<"\nvector:\t";
for(int i=0; i<temp.size();i++)
{
if(temp[i]==1)
{
cout<<v[i]<<" ";
}
}
cout<<"\n\n";
}while(next_permutation(temp.begin(),temp.end()));
}
https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42839
위 문제에서 사
pair
헤더
#include <utility> // 그러나 vector, algorithm에 포함되어 있음선언
pair<int, int> p;인자 접근
p.first=1;
p.second=2;
p1=make_pair(1,2);
벡터 안에 pair 넣어서 사용
vector <pair<int, int>> v;
v.push_back(make_pair(2,1));'언어 공부 > C++' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++/코딩테스트] 프로그래머스: 다리를 지나는 트럭 (0) | 2023.05.11 |
|---|